FunDoRoo™ is a physical activity curriculum developed and tested to improve motor skills of youth with and without developmental disabilities.
This physical activity curriculum was implemented at home by parents during six months and led to improvements in motor skills such as body coordination, strength & agility.
The FunDoRoo mobile app has three components: Activities, Daily Plans, and Tools.
The Activities feature includes images and written descriptions as well as demo videos of each of activities in three categories: body preparation (warm-up), strengthening (muscle and bone building) and games. The text descriptions of the activities, in combination with the illustrations, provide a complete reference as to how to lead each activity, including the sports equipment needed. The videos feature step-by-step instructions on how to set-up and carry out the activities, and show adults and children doing activities together in small indoor spaces as well as in the outdoor setting. The activities and games shown in the videos are demonstrated by youth with and without developmental disabilities and their families, a physical activity instructor, and do not include actors.
In the Daily Plans feature, FunDoRoo has lesson/activity plans that are 25-45+ minutes long. The 50 pre-made plans include the activities from the curriculum. The plans follow a progression for duration as well as for difficulty of the included activities. The plans indicate as well the total estimated duration and whether they are better suited for small spaces or if little equipment is needed. It is also possible to customize and design new lesson plans within a few clicks.
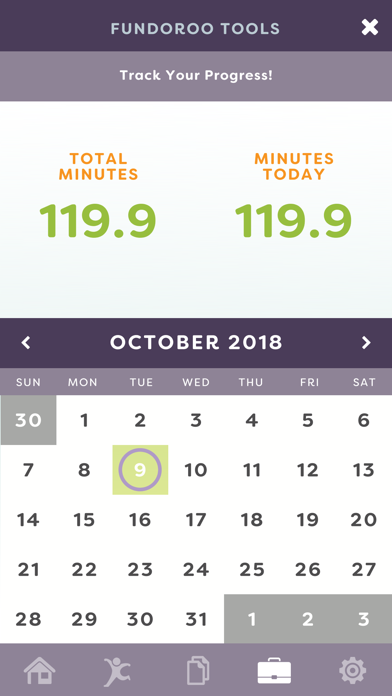
The Tools feature includes videos and tutorials as to how to use the mobile application, how to modify activities, how to create your own plan, safety measures to avoid injuries, and a tracking calendar. The content of FunDoRoo mobile application has been submitted for copyright for intellectual property.
What is different about FunDoRoo from other mobile applications?
FunDoRoo was based on the principle that children should enjoy movement and being active should be fun, interesting and challenging. All of the activities included in FunDoRoo have game-like situations. All games have been designed so they can be played by one child and one adult but can be played by more players! The games and activities have recommendations as to how to make them less or more challenging, and can be adapted to players of different skill levels.
While when we designed FunDoRoo we thought of parents and children being active together; this mobile application can also be used by physical educators, physical therapists, or anybody leading physical activity for children.
Try for yourself using FunDoRoo to have a fun physical activity routine with your family and then let us know what you think! We hope you enjoy begin physically active together as a family.
Publications related to the contents of FunDoRoo:
Rubin, DA, Duran, AT, Haqq, AM, Gertz, E, Dumont-Driscoll, M. Changes in Cardiometabolic
Markers in Children with Prader-Willi Syndrome and Nonsyndromic Obesity following
Participation in a Home-Based Physical Activity Intervention. Pediatric Obesity. In press.
Rubin, DA, Wilson, KS, Honea, KE, Castner, DM, McGarrah, JG, Rose, DJ, Dumont-Driscoll, M.
An evaluation of the implementation of a parent-led, games-based physical activity intervention: the Active Play at Home quasi-randomized trial. Health Education Research. In press.
Rubin, DA, Wilson, KS, Rose, DJ, Wiersma, LD, Dumont-Driscoll M. (2016). Implementation of a home-based physical activity curriculum in children with and without Prader-Willi Syndrome. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 48(5 Suppl 1):768. doi: 10.1249/01.mss.0000487306.43573.4c.
Rubin, DA, Wilson, KS, Wiersma, LD, Weiss, JW. and Rose, DJ. (2014) Rationale and design of active play @ home: a parent-led physical activity program for children with and without disability. BMC Pediatrics,14:41.